“Defining the environmental context in which genes enhance disease susceptibility can provide insight into the pathogenesis of complex disorders. We report that the intra-uterine environment modulates the association of schizophrenia with genomic risk (in this study, genome-wide association study–derived polygenic risk scores (PRSs)).”
.
“In independent samples from the United States, Italy, and Germany, the liability of schizophrenia explained by polygenic risk scores is more than five times greater in the presence of early-life complications compared with their absence.”
.
“Patients with early-life complications histories have significantly higher polygenic risk scores than patients without early-life complications histories, which is confirmed in additional samples from Germany and Japan. The gene set composed of schizophrenia loci that interact with early-life complications is highly expressed in placenta, is differentially expressed in placentae from complicated in comparison with normal pregnancies, and is differentially upregulated in placentae from male compared with female offspring.”
.
“Pathway analyses reveal that genes driving the polygenic risk scores-early-life complications interaction are involved in cellular stress response…..”
.
“We conclude that a subset of the most significant genetic variants associated with schizophrenia converge on a developmental trajectory sensitive to events that affect the placental response to stress, which may offer insights into sex biases and primary prevention.”
.
G.Ursini, et al
Convergence of placenta biology and genetic risk for schizophrenia
Nature Medicine — Volume 27 #6 — June 2018 — page 792
.
.
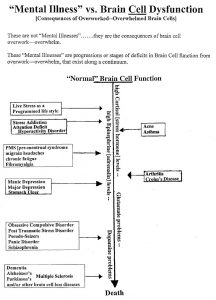
TheETG repair of brain cell overwork, overwhelm, “mental illness” —–
https://theetgtrackclub.com/documents/TheETGbrain.pdf